Gallstones:
- Why we get gallstones
- Symptoms
- Complications of gallstones
- Diagnosis
- Non-surgical treatments
- Surgery
- Life after cholecystectomy
The diagnosis of gallstones begins with the raising of the possibility of their presence from talking to and examining the patient.
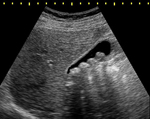 Ultrasound - This examination utilises the ability of sound waves to penetrate the tissues of the abdomen to produce an image of the gall bladder on a screen. In the image the stones are visible within the gall bladder and can be seen to cast a shadow.
Ultrasound - This examination utilises the ability of sound waves to penetrate the tissues of the abdomen to produce an image of the gall bladder on a screen. In the image the stones are visible within the gall bladder and can be seen to cast a shadow.
The size of the ducts and any stones within them can also be assessed.
The advantage of ultrasound is rapidity and patient acceptability.
Its disadvantage is that images are difficult to interpret in the obese and gaseous patients.
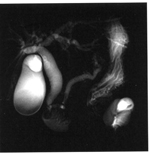 MRCP - An MRI scan can recreate in three dimensions the liver, bile ducts and pancreas in cases where the ultrasound is not clear.
MRCP - An MRI scan can recreate in three dimensions the liver, bile ducts and pancreas in cases where the ultrasound is not clear.
The images are produced by using the patient's bile as a contrast medium. The results are generated without radiation or invasive procedure.
The images may be rotated and viewed at any angle to carefully examine the bile ducts for stones or other abnormality.
The disadvantages of this technique are that the MR scan may be lengthy and that scan cannot remove the stones, if seen. It is undoubtedly safer, however, than an ERCP.
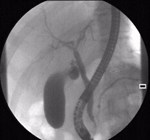 ERCP -This is an invasive examination using a special endoscope.
ERCP -This is an invasive examination using a special endoscope.
Dye is injected into the bile duct and X-ray images produced of the bile and pancreatic ducts.
Any escaped stones may be crushed or removed at the same time as their diagnosis using specialised baskets.
This procedure may precede the cholecystectomy in patients who are jaundiced or diagnosed with bile duct stones.
A small number of patients (about 10%) will develop pancreatitis following injection of dye into the pancreatic duct. Occasionally this may be severe.